Through Hole Application in Reverse Engineering PCB is quite common, especially when redraw the printed circuit board gerber file documents, through hole is also being viewed as VIA which is one of the important components of multilayer PCBs.
Through Hole Application in Reverse Engineering PCB is quite common, especially when redraw the printed circuit board gerber file documents, through hole is also being viewed as VIA which is one of the important components of multilayer PCBs
The cost of drilling holes usually accounts for 30% to 40% of the cost of PCB card remanufacturing. Simply put, each hole on the PCB can be called a via.
From a functional perspective, vias can be divided into two categories: one is used as an electrical connection between layers; the other is used for fixing or positioning devices.
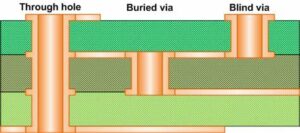
In terms of process, these vias are generally divided into three categories, namely blind vias, buried vias, and through vias.
The blind holes are located on the top and bottom surfaces of the printed circuit board and have a certain depth. They are used to connect the surface layer circuit and the inner layer circuit below. The depth of the hole usually does not exceed a certain ratio (aperture).
Buried hole refers to the connection hole located in the inner layer of the printed circuit board, it will not extend to the surface of the circuit board. The above two types of holes are located in the inner layer of the circuit board, and are completed by a through-hole molding process before lamination, and several inner layers may be overlapped during the formation of the via hole.
The third type is called a through hole. This hole penetrates the entire circuit board and can be used for internal interconnection or as a positioning hole for component installation. Because through-holes are easier to implement and lower in cost, most printed circuit boards use it instead of the other two vias. The vias mentioned below are considered as through holes unless otherwise specified.






