How to Read PCB Schematic Diagram Swiftly, first of all we need to figure out what is a schematic? The schematic diagram, also known as the circuitry diagram, is a drawing that reflects the electrical connections of the various components in the assembled printed circuit board. The circuit diagram consists of some abstract symbols and rules. Through the analysis and research of the schematic diagram, we can understand the circuit structure and working principle of the assembled PCB board, and lay a solid foundation for enabling it. As a hardware design engineer, what can we read from a schematic?
- The logical block diagram of the system. In the first few pages of the schematic, the block diagram of the system is described, which is composed of large blocks.
- The system’s power, clock, and reset diagrams.
- The connection relationship of the various components of the motherboard, the model of the device, and so on. When we don’t know the specific device features, the detailed model allows us to search the hardware manual on the Internet to quickly understand its approximate function.
- GPIO, PCI device IRQ. PCI devices are gradually being phased out. PCIE device interrupts are determined by sending the message (msg), which is determined by the chip’s IRQ Swizzling (not covered in this article), and the schematic no longer reflects this information. However, with the expansion of the IA32 application range, the number of GPIOs has become more and more, from dozens to hundreds, so that it can flexibly respond to various application scenarios. At the same time, in order to control the size of the chip and reduce the number of pins, the GPIO is often multiplexed with the function module inside the SOC. Correctly configuring the multiplex (MUX) register is the responsibility of the firmware. The required information is from the schematic. Come in.
- Jumper, PCIE slot connection and so on.
The information contained in the schematic is very rich. Studying schematics is often the first step in enabling us to design a PCB board. Let’s get started soon.
Composition
A complete circuit diagram is composed of several elements, including graphic symbols, text symbols, links, and annotative characters.
Graphic symbol
Graphic symbols are the main components that make up a circuit diagram. For example, a small rectangle means a resistor.
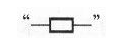
Two short bars indicate capacitors
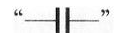
Continuous semicircle representing the inductor







