It is generally believed that MOSFET (MOS tube) is driven by voltage and does not require driving current. However, there is a junction capacitance between the G pole and the S pole of the Mosfet, and this capacitance will make it difficult to drive the MOS. The three capacitors in the figure below are the junction capacitance of the Mosfet, and the inductance is the parasitic inductance of the circuit trace:
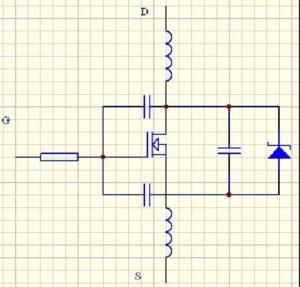
junction capacitance of the Mosfet
If the ripple, EMI and inrush current requirements are not considered, the faster the switching speed of the Mosfet, the better.
Because the shorter the switching time, the smaller the switching loss, and the switching loss accounts for a large part of the total loss in the switching power supply, so the quality of the MOS tube drive circuit directly determines the efficiency of the power supply.
How to quickly turn on and turn off the Mosfet? For a Mosfet, the shorter the time it takes to pull the voltage between GS from 0 to the turn-on voltage of the tube, the faster the turn-on speed of the Mosfet will be. Similarly, if the GS voltage of the Mosfet is reduced from the turn-on voltage to 0V, the shorter the time, the faster the turn-off speed of the MOS tube is.






