PCB Card Reverse Engineering will help to reduces unnecessary costs associated with troubleshooting and rework. In PCB Card Reverse Engineering, due to the use of transient voltage suppressor (TVS) diodes to suppress direct charge injection due to ESD discharge, it is more important in PCB Card Reverse Engineering to overcome the electromagnetic interference (EMI) electromagnetic field effect of the discharge current. This article will provide PCB design guidelines that can optimize ESD protection.
ESD Suppresion in PCB Card Reverse Engineering
Current is induced into the circuit loop by induction, and these loops are closed and have varying magnetic flux. The magnitude of the current is proportional to the area of the loop. Larger loops contain more magnetic flux and thus induce a stronger current in the circuit. Therefore, the loop area must be reduced.
The most common loop is shown in below Figure, which is formed by the power supply and ground. Where possible, multilayer PCB designs with power and ground planes can be used.
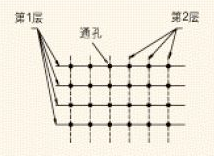
The multi-layer board not only minimizes the loop area between the power supply and ground, but also reduces the high frequency EMI electromagnetic field generated by the ESD pulse. If a multilayer board cannot be used, the lines for the power line and ground must be connected in a grid as shown in below Figure.
The grid connection can function as a power and ground plane. Use vias to connect the traces of each layer. The via connection spacing should be within 6 cm in each direction. In addition, when wiring, the power supply and ground traces as close as possible can also reduce the loop area.
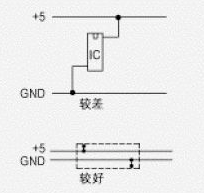
Another way to reduce loop area and induce current is to reduce parallel paths between interconnected devices. When a signal cable longer than 30 cm must be used, a protective wire can be used, as shown in FIG.
A better approach is to place the formation near the signal line. The signal line should be within 13 mm of the protective or ground plane. As shown in Figure 6, the long signal line (>30 cm) or the power line of each sensitive component is placed across its ground line. Crossed lines must be arranged at regular intervals from top to bottom or left to right.






