Clone Automobile PCB Board Thermal Management System is the most critical points that affects reliability (in terms of performance here) is heat. Integrated circuit (IC) overheating can become problematic over time, and the automotive environment can become very unforgiving. For example, overheating components in an engine bay, or driving through climates ranging from winter in Michigan to summer in Arizona.
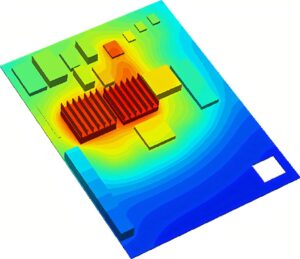
Clone Automobile PCB Board Thermal Management System
From the IC package, through the PCB, to the complete product in the operating environment, heat should be controlled. So we need to use the virtual prototyping for simulation feature all the way through all stages of design to ensure we have a thermally reliable product.
First, IC suppliers typically analyze component packaging and provide thermal characterization models. Next we wanted to analyze the stand-alone PCB as the design unfolded. PCB designers often require analysis of the layout of their working parts to determine if they have made a pc board that is difficult to cool.
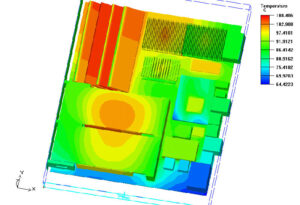
PCB designers often require analysis of the layout of their working parts to determine if they have made a pc board that is difficult to cool.
And this work is not just a rough consideration of the PCB board heat dissipation and location distribution with the printed circuit board. Since there are many heat-dissipation paths (heat sink, inner copper, transfer, conduction, and divergence…) when we Clone Automobile PCB Board Thermal Management System, the data passed from the PCB board thermal design system to the thermal analysis must be complete. The setup and execution of the analysis software must also be fairly intuitive, as you want the PCB designer using the software not necessarily to be a thermal expert and not delay the design process.






