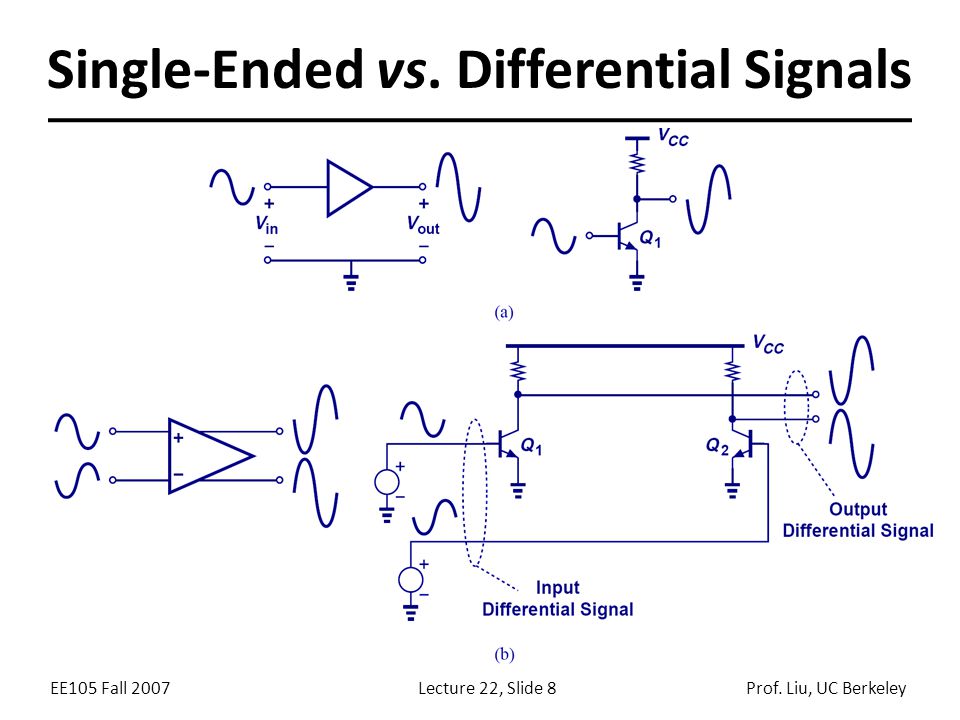
Differential signals are so widely used because of their many advantages over single-ended signals.
as follows:
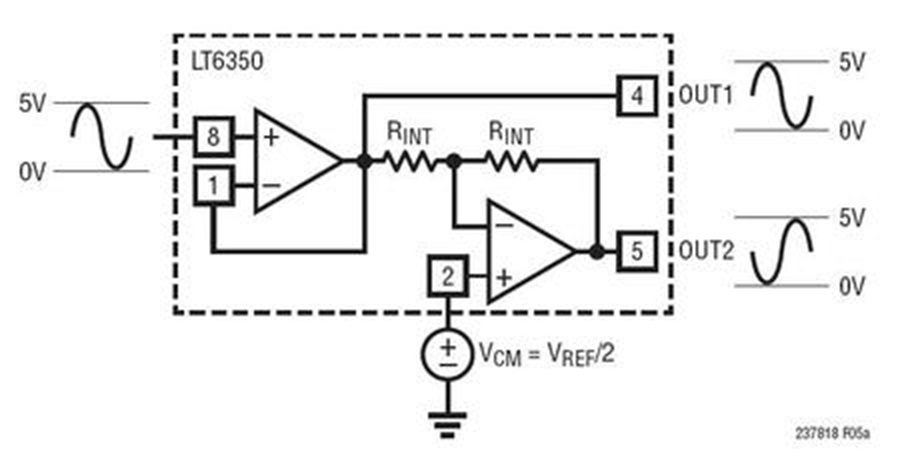
1, The differential circuit is very useful when the signal amplitude is small. If the amplitude of the signal is small, or the signal-to-noise ratio is very high, applying a differential signal can effectively double the signal amplitude. Differential and differential amplifiers are commonly used in the input stage of small signal systems.
2, Since the differential signals are equal in magnitude, the reflow signal does not appear on other paths. If there is no back-flow signal, then the continuity of the ground path becomes unimportant. The use of differential devices makes isolation of the power system easier.
3, The differential receiver is sensitive to differences in the input signal and is not sensitive to the similarities of the input signals. Therefore, the differential circuit is naturally immune to the common mode signal.
4, Timing positioning is accurate. Since the switching change of the differential signal is located at the intersection of the two signals, unlike the ordinary single-ended signal, which depends on the high and low threshold voltages, it is less affected by the process and temperature, which can reduce the timing error.
The biggest disadvantage of differential signals is the potential for Electro-Magnetic Interference. If the differential signal is not properly balanced or filtered, or if there is any common-mode signal, the differential signal applied to the external twisted pair may cause Electro-Magnetic Interference problems.
The second drawback is that transmission of differential signals requires twice as many signal lines as compared to single-ended signal transmission, and many new principles and important PCB board design rules are understood to greatly increase PCB design complexity.






