With the continuous improvement of the working speed of electronic circuit boards and the requirements for higher data transmission rates, the traditional lumped circuit parameter model has also been replaced by distributed circuit parameter models, and circuit boards designers are increasingly shifting their attention. How to overcome various signal integrity problems that occur in high-speed circuit operation especially the High Speed Digital Circuit Board Design Differential Signal Transmission.
Modern high speed circuit boards often use differential lines as carriers for high-speed signals. Today less than 50% of circuit boards use differential pairs. It is expected that over 90% of boards will use differential transmission lines and these differential lines in the next few years will become the main interconnect structure of high-end, high-speed Printed Circuit Board, it can be seen that the study of differential transmission lines has important significance.
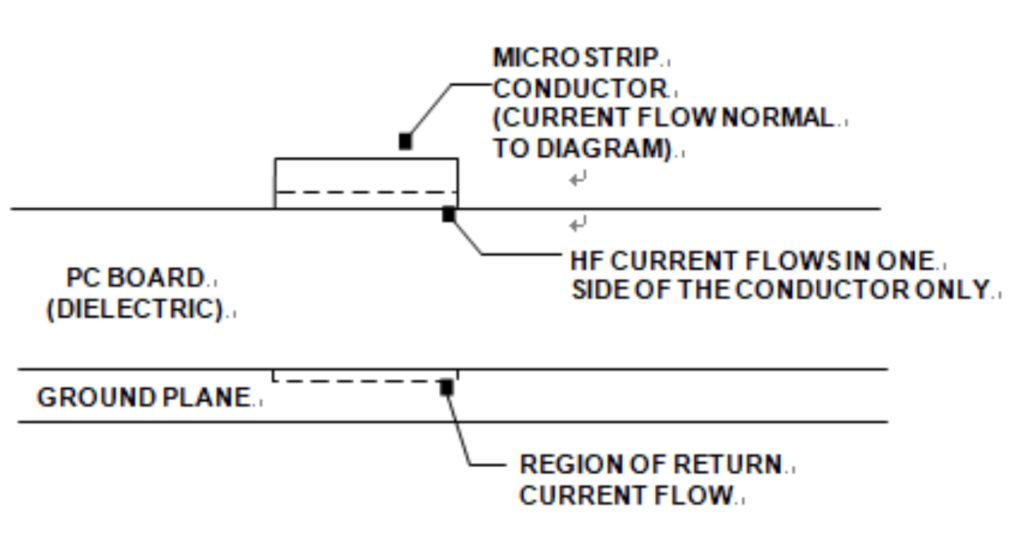
A differential pair is a pair of transmission lines that are coupled together. The significance of applying a pair of transmission lines is not so much the use of the characteristics of the differential pair, but rather the characteristics of the differential signal, which is achieved by the differential pair. Differential signal transmission uses two output drivers to drive two transmission lines.
One carries the signal and the other carries its complementary signal. The signal required is the voltage difference between the two transmission lines, which carries the information to be transmitted. Differential signals are widely used in small computer Scalable Interface (SCSI) buses and Ethernet, and are also used in fiber optic telecommunications protocols such as OC-48, OC-192, OC-768, and in communication which use twisted-pair lines as main carrier.






